What Is Thunderbolt 3?
Despite being developed by Intel, Thunderbolt is a hardware interface that’s more commonly associated with Apple than PCs. But that’s slowly changing as new Windows 10 notebooks are being fitted with Thunderbolt 3 ports. In this article, I’ll explain what Thunderbolt 3 is and where USB Type-C connectors fit into the picture.

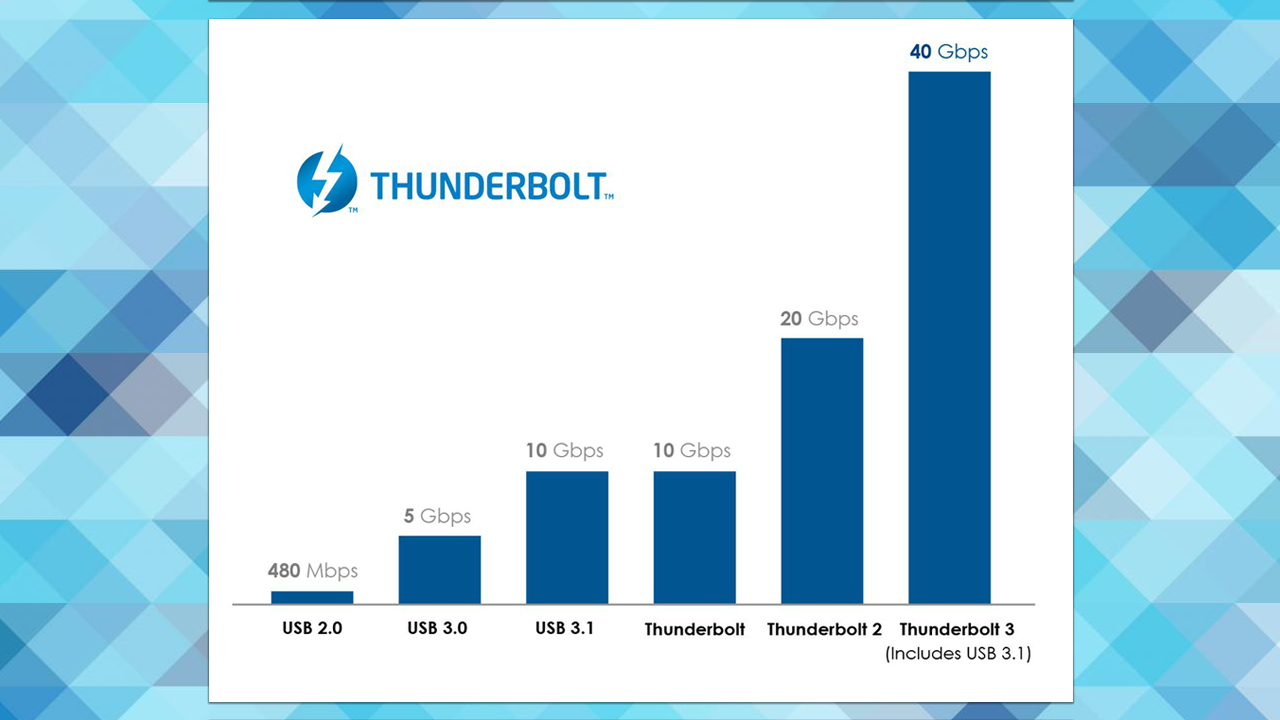
Thunderbolt is a technology designed to allow you to connect peripherals to your PC and other devices, while at the same time solving some of the problems associated with USB and Firewire. Offering speeds of up to 40 Gb/s, it’s twice as fast as Thunderbolt 2 and four times faster than USB 3.1.
Cables and Connectors
Apart from the significant increase in speed, Thunderbolt 3 addresses a major concern that stopped the technology from being widely adopted in the past. Thunderbolt 2 required a Thunderbolt cable, but Thunderbolt 3 uses USB Type-C cables, with the new 24-pin reversible connectors that will eventually supersede USB Type-A and B.
But Thunderbolt 3 and USB Type-C cables, while utilizing the same connector, are the same but different. And this is where it starts to get a little confusing. Thunderbolt 3 cables will come in three different flavors to suit user needs. A standard copper USB Type-C cable can be used to connect devices to Thunderbolt 3 ports, but are limited to transfer rates of up to 20 Gb/s. A second type of copper USB Type-C cable will allow transfer rates of up to 40 Gb/s, and finally a third optical USB Type-C cable will allow up to 40 Gb/s over long distances.
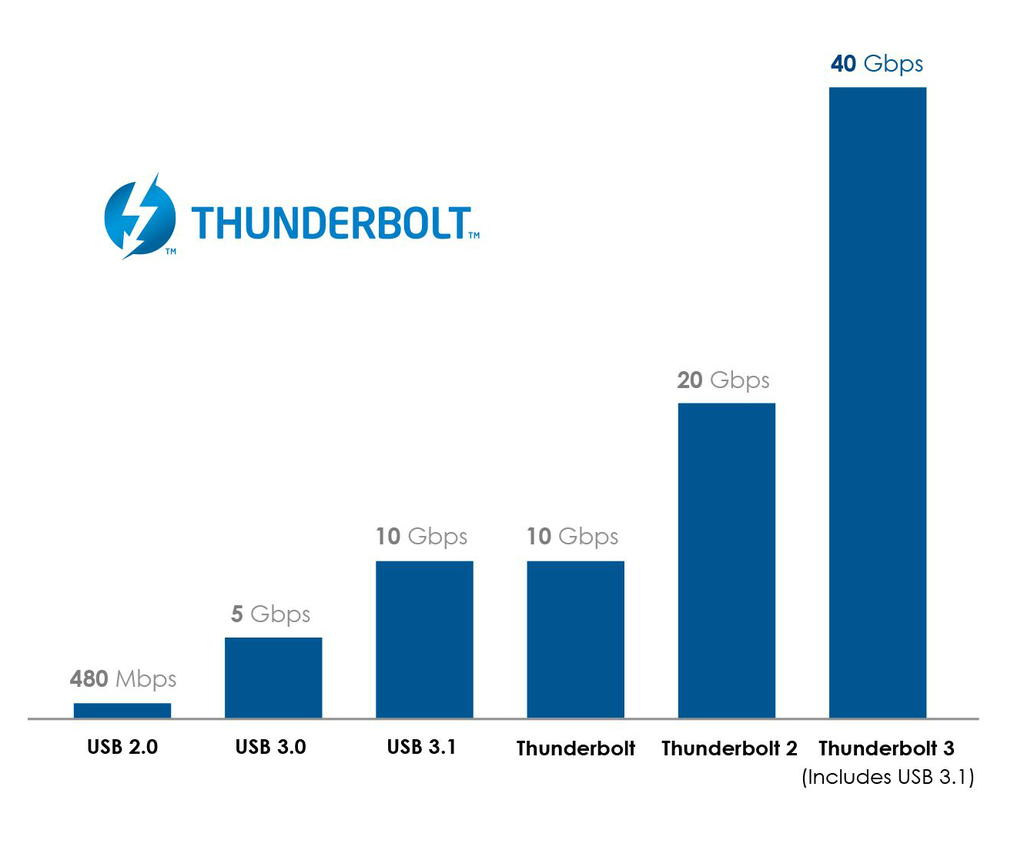
In short, if you want a cable that’s capable of the maximum transfer rate of 40 Gb/s, search for a Thunderbolt 3 cable and check the transfer rate. Other USB Type-C cables might not offer maximum speeds for Thunderbolt and most Thunderbolt 3 cables available today support only 20 Gb/s transfer rates. Additionally, optical USB cables are not currently available but are due to start shipping this year, so watch this space.
Thunderbolt 3 Uses
Thunderbolt 3 can run two Quad HD (4K) displays simultaneously and is replacing HDMI and DisplayPort on new devices. Docking stations with charging and standard USB devices are also supported. Thunderbolt Networking allows Ethernet connections to be created between devices for 10 Gb/s data transfers. And if that wasn’t enough, there’s up to 100 watts system charging and 15 watts for bus-powered devices.
Although new devices will come with just one Thunderbolt, the technology allows daisy chaining of up to 6 devices. And companies like Dell and Microsoft are producing hubs that can be used as docking stations. For instance, I use Microsoft’s Display Dock to connect a Full HD display, mouse and keyboard to my notebook via its Thunderbolt port – even though the Display Dock is primarily designed to be a Continuum hub for Windows 10 Mobile.
Dell produces a true Thunderbolt dock in the form of the Dell Thunderbolt Dock TB15, which supports up to three Full HD displays or two 4K displays at 60Hz, unlike the Microsoft Display Dock which is limited to one Full HD display, and transfer speeds of up to 40 Gb/s.
Thunderbolt 3 and USB Type-C connectors are by no means everywhere yet, but over the next couple of years, smartphones, tablets, and notebooks are going to see USB Type-C and Thunderbolt ports become a common standard.