How to Use Server Manager in Microsoft Azure to Manage Servers
The default Windows Remote Management (winrm) settings in Microsoft Azure VMs, i.e. those provisioned using templates from the gallery, prevent Server Manager from connecting to other servers on your Azure virtual network. In this Ask the Admin, I’ll show you how to use Server Manager in Windows Azure and how to quickly return the default winrm configuration.
Configure Windows Remote Management Listener on HTTP
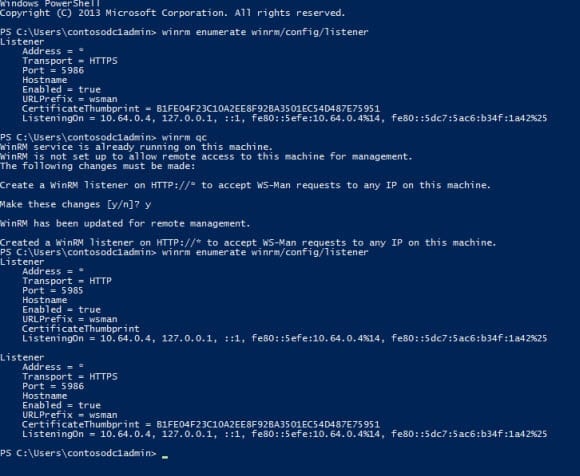
By default, Windows Remote Management (winrm) is enabled out-of-the-box in Windows Server 2012 R2 with an HTTP listener. However, if you open a command prompt on an Azure VM and run winrm enumerate winrm/config/listener, you’ll see that it’s configured to listen on HTTPS.
To manage a remote server using Server Manager, we need to configure an HTTP winrm listener on each remote server, which can be achieved by running winrm qc from an elevated command prompt. You’ll be prompted to confirm that you want to create a new listener, as shown in the figure below.
Add Remote Servers to Server Manager
Once winrm is configured to support Server Manager on each remote server, on your management server, you can add the remote server(s) to Server Manager.
- Start Server Manager from the Start screen or taskbar icon.
- Select Add Servers from the Manage menu.
- In the Add Servers dialog, click Find Now on the Active Directory tab.
- Select the server(s) you want to add to Server Manager and click the arrow in the center of the dialog.
- Click OK to complete the process.
Now if you go to the Server Manager dashboard and refresh the view, you should see the remote servers appear as part of the summary information.



