Configuring Cluster-Aware Updating in Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 (WS2012) introduced Cluster-Aware Updating (CAU) to allow each member of a cluster be paused, drained of highly available (HA) roles, patched, and rebooted in an orchestrated manner. Without CAU, you will probably be patching your clusters manually (which rarely happens), and in the case of Hyper-V clusters, CAU will leverage Live Migration to ensure that services have zero downtime.
We will be implementing a number of steps:
- Prerequisites: Getting the environment and servers ready
- Prestaging a computer account: This will be for a HA role that is used by the cluster to orchestrate the CAU patching process.
- Configuring CAU
- Testing and monitoring CAU patching
CAU Prerequisites
There are a number of prerequisites for installing and maintaining CAU on your clusters. Each cluster node should be configured with:
- Enabled WMI: This is the default on WS2012. You can run Set-WSManQuickConfig to enable WMI if it is disabled.
- Enable Windows PowerShell 3.0 and Windows Powershell remoting: This is also the default on WS2012. PowerShell is a Server Manager role, and you can use Enable-PSRemoting to enable remoting.
- .Net 4.5: This is also installed by default (Server Manager) on WS2012.
- Remote Shutdown firewall rule: You must enable the Remote Shutdown inbound rule in Windows Firewall. The PowerShell option is Set-NetFirewallRule -Group “@firewallapi.dll,-36751” -Profile Domain -Enabled true.
You will need a location for your nodes from which to download the updates. Unfortunately System Center Configuration Manager does not support CAU yet. The recommended managed solution will be to use WSUS. If you are downloading updates through a proxy (such as directly from Microsoft) then you will need to configure WinHTTP proxy settings on each cluster node. This would be done as follows, with a proxy called TheProxy.Demo.Internal that operates on TCP 80:
netsh winhttp set proxy TheProxy.Demo.Internal:80 “<local>”
Prestaging a Computer Account
CAU will require a computer account that will be used by the cluster to create a HA role that enables the cluster to self-manage the orchestrated patching, even if the nodes of the cluster are being rebooted. The setup wizard does allow you to let the cluster create a computer account in Active Directory, but this will get some anonymous name. Take the time to create a prestaged computer account with a name that will mean something to you and your colleagues in a year’s time.
- Place all cluster nodes and the cluster client access point (CAP) computer account into an OU, preferably named after the cluster. For example, the cluster CAP is called Demo-FSC2. An OU called Demo-FSC2 is created. The members of the cluster (Demo-FS1 and Demo-FS2) and the CAP (Demo-FSC2) are moved into the new OU.
- Create a computer account in the new OU and give it a meaningful name. This will be the prestaged computer account. For example, it could be called Demo-FSC2-CAU, indicating that the account is used by CAU on the Demo-FSC2 cluster.
- Disable (not delete) the new computer account.
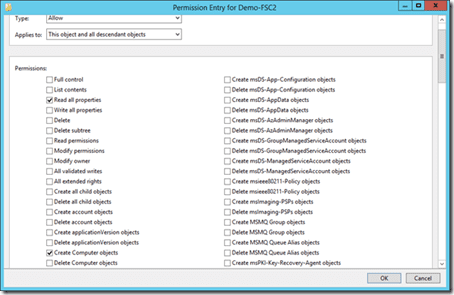
- Enabled the Advanced view in Active Directory Users And Computers. Edit the security (via the Advanced button) of the cluster’s OU. Grant the cluster CAP (in our case, Demo-FSC2) List All Properties and Create Computer Account permissions to This Object And All Descendent Objects.
The prestaged computer account and cluster accounts.
Granting the cluster permissions to the cluster’s OU.
Configure CAU
Now you will open up Failover Cluster Manager (FCM) and configure CAU for your cluster:
- Browse to the cluster in FCM and launch Cluster-Aware Updating from the Configure pane.
- Click the Configure Cluster Self-Updating Options link in the Cluster-Aware Updating wizard.
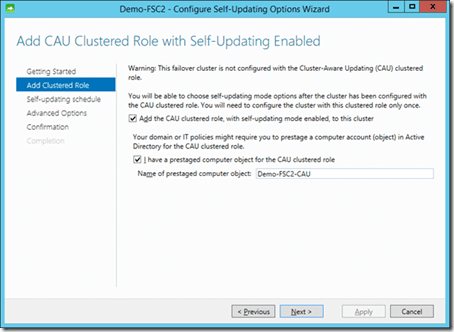
- In the Add-Clustered Role step of the wizard, check the box for Add The CAU Clustered Role box and also check the I Have A Prestaged Computer Object box.
- Type in the name of the prestaged computer account, for example Demo-FSC2-CAU.
- Configure when you want CAU to run in the Self-Updating Schedule step. You can choose a daily, weekly, or monthly day/time. In the case of Hyper-V, many will choose to run CAU during a midweek workday; this is because there is no perceivable downtime for virtual machine services and engineers/administrators will be on hand to monitor operations instead of being woken at 5 a.m. on a Sunday morning if a drained host had a problem.
- The Advanced Options wizard step allows you to customize how CAU runs. This includes how many failed hosts will be tolerated, retry attempts (three by default), a patching timeout (very dangerous, because you don’t want half-patched servers), and various kinds of scripts that can be run.
- Additional Options allows you to include recommended updates, which is… well, recommended.
Using the prestaged computer account.
If all goes well the wizard will complete with a Success status. Check the prerequisites, the name of the prestaged computer account, and the permissions on the cluster’s OU.
Testing and Monitoring CAU
With CAU configured, your cluster will automatically:
- Drain each node, using live migration in the case of Hyper-V
- Patch it
- Reboot it if required (it usually is)
- Repeat the process with each node in turn
You can initiate a patch run manually from FCM on a cluster node once you have completed the above configuration. Launch the Cluster-Aware Updating Wizard and then run Apply Updates To This Cluster. The status of the update job will be visible under Log Of Updates In Progress. You can also run Generate Report On Past Updating Runs from a specific time window, with the added option of exporting the report in HTML format.
Warning: WS2012 Hyper-V VMs with Low Priority
By default WS2012 Hyper-V uses Quick Migration on virtual machines with a low cluster priority. You can change this default behaviour so that low priority VMs are moved using live migration, just like medium- and high-priority VMs. WS2012 R2 Hyper-V uses live migration by default for VMs of all priorities.