Managing Windows 2008 Server Core through RDP
As described in my previous articles, Windows Server 2008 has an interesting option to install it with a minimal graphical user interface (or GUI for short). This method of installation is called “Server Core”, and it allows an administrator to only install the minimum binaries required to run a specific server role (currently, there are 9 possible Server Core roles). You can read more about it on my “Understanding Windows Server 2008 Server Core” article.
Although Server Core has no real GUI (except a few tools such as Task Manager), we still need to access it locally in order to run configuration and diagnostic commands on it. Some of these commands are accessible via remote MMC snap-ins, run from remote management workstations or servers. However, some commands need to be run only on the local Command Prompt, causing us to need to physically have access to the Server Core server.
This can be avoided by enabling the machine running Server Core to allow us to remotely connect to it by using the Remote Desktop Protocol client, also known as mstsc. But before we can use it to connect to the machine, we need to make sure the following issues have been dealt with. These requirements are:
- Configuring an IP address
- Configuring a server name
- Configuring an administrator’s password
- Configured the server’s firewall
You should, but are not required to, also join the server to your domain.
Next, in order to properly configure Server Core to allow ICMP replies, follow these steps:
To manage a server running a Server Core installation by using a terminal server client
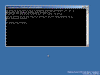
- On the server running a Server Core installation, type the following command at a command prompt:
cscript C:\Windows\System32\Scregedit.wsf /ar 0
This enables the Remote Desktop for Administration mode to accept connections. BTW, in order to view your current settings you can type:
cscript C:\Windows\System32\Scregedit.wsf /ar /v
If you see “1” in the script output, that means that RDP connections are denied. If you see a “0”, they will be allowed. Note: If you are running the Terminal Services client on a previous version of Windows, you must turn off the higher security level that is set by default in Windows Server 2008. To do this, type the following command at the command prompt:
cscript C:\Windows\System32\Scregedit.wsf /cs 0
To enable remote management from an RDP connection through the firewall
- To enable remote management from any MMC snap-in, type the following:
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="Remote Desktop" new enable=yes
To open an RDP session with the Server Core machine
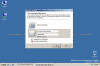
- On the remote management computer, click Start > Run, type mstsc, and then click OK.
- In Computer, enter the name of the server running a Server Core installation, and click Connect.
- Log on using an administrator account.
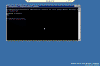
- When the command prompt appears, you can manage the computer using the Windows command-line tools.
Note that while you’re logged on to the server, the original server console session is locked out.
- When you have finished remotely managing the computer, type logoff in the command prompt to end your Terminal Server session.
Summary
Windows Server 2008 Server Core installations, like any other servers, require remote management. In order to allow for that, the server’s Firewall and registry settings need to be changed. This article showed you how to do that.
Recent Windows Server 2008 Forum threads
Got a question? Post it on our Windows Server 2008 forums!